Annex A
(informative)
Examples of protection in case of direct contact
A.1 General
Figures A.1 to A.3 show examples of the methods used for protection in case of direct contact
(see 4.3.4).
Protection against direct contact
Protective separation from circuits requiring protection against direct
contact
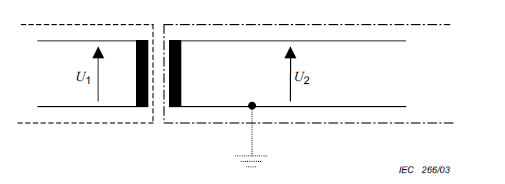
A.2 Protection by means of DVC A
See (4.3.4.2.)

Key
U1: hazardous voltage, earthed or unearthed.
U2: ≤ 30 V a.c.
Figure A.1 – Protection by DVC A,
with protective separation
A.3 Protection by means of protective impedance
(See 4.3.4.3.)
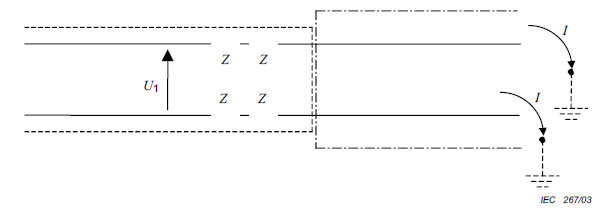
Key
U1: hazardous voltage, earthed or unearthed.
I ≤ 3,5 mA a.c., 10 mA d.c.
NOTE To provide protection in single-fault conditions, I = U1/Z
Figure A.2 – Protection by means of protective impedance
A.4 Protection by using limited voltages
(See 4.3.4.4.)
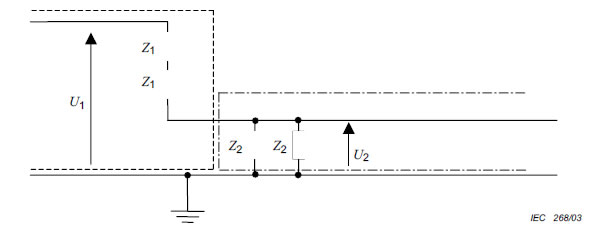
Key
U1: hazardous voltage, earthed.
U2: ≤ 30 V a.c., 60 V d.c.
NOTE To provide protection in single-fault conditions, U2 = U1Z2/(2Z1 + Z2) or U2 = U1Z2/2(Z1 + Z2/2).
Figure A.3 – Protection by using limited voltages