Annex E
(informative)
Methodology for the estimation of susceptibility
to common cause failures (CCF)
E.1General
This informative annex provides two simple qualitative approaches for the estimation of CCF
that can be applied to the subsystem design.
E.2 Methodology
E.2.1Requirements for CCF
A comprehensive procedure for measures against CCF for sensors/actuators and separately
for control logic is given, for example, in IEC 61508-6:2010, Annex D. Not all measures given
therein are applicable to the machinery application. The most important measures are given
here.
NOTE It is assumed that for redundant systems a β-factor according to IEC 61508-6:2010, Annex D is less than or
equal to 2 %.
E.2.2 Estimation of effect of CCF
This quantitative process should be passed for the whole system. Every part of the safety-
related parts of the control system should be considered.
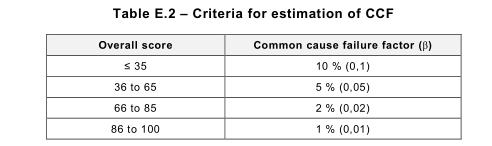
Table E.1lists the measures and contains associated values, based on engineering judgement,
which represent the contribution each measure makes in the reduction of common cause
failures. For each listed measure, only the full score or nothing can be claimed. If a measure is
only partly fulfilled, the score according to this measure is zero.
Using Table E.1, those items that are considered to affect the subsystem design should be
added to provide an overall score for the design that is to be implemented. Where it can be
shown that equivalent means of avoiding of CCF can be achieved through the use of specific
design measures (e.g. the use of opto-isolated devices rather than shielded cables), then the
relevant score can be claimed as this can be considered to provide the same contribution to the
avoidance of CCF.
It is expected that the references 9, 11, 12 and 13 are always addressed unless it can be
justified.
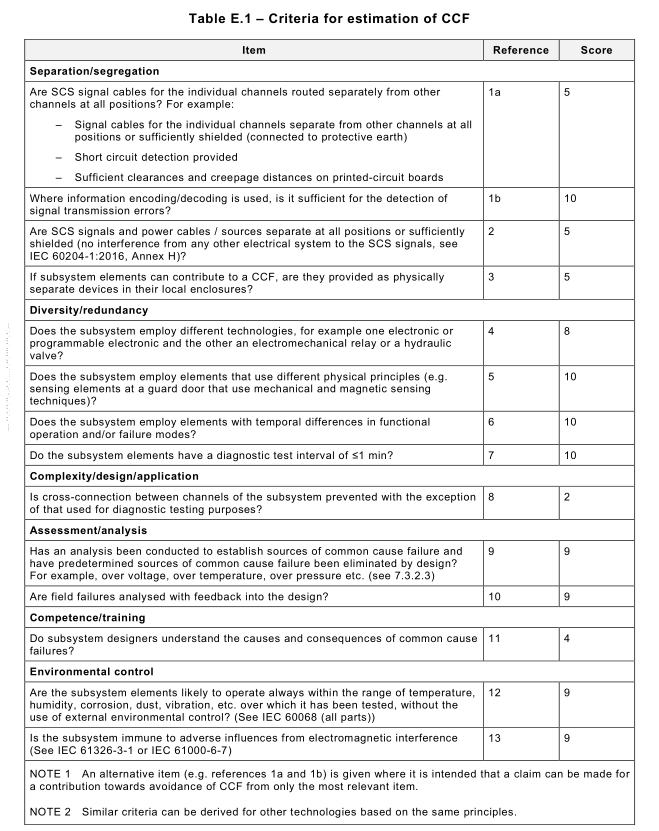
This overall score can be used to determine a common cause failure factor (β) using Table E.2.